Main Causes and How to Identify Them
It’s frustrating when you’ve spent time and effort optimizing your site, only for Google not to index certain pages. Especially when those issues don’t have an obvious explanation.
But ignoring the problem isn’t an option. So, what do you do if some of your important pages aren’t appearing in search results? You delve into the ‘why.’
In this article, I’ll explain the most common causes of indexing problems. I’ll also discuss potential solutions and recommend some tools. But first, let me explain exactly what indexation is about.
What is Indexation in SEO?
Indexation is the process of analyzing content on a web page and storing it in a database or index. Once a page is indexed, users can easily find it using relevant search queries.
The Importance of Proper Indexation for Your Website
Proper indexation is a key health metric for every website. It increases the legitimacy and authority of your site and lets you acquire new customers for your business. On the other hand, improper indexation can lead to difficulties in customer acquisition. If you have unaddressed indexing issues on your site, you will lose out to competitors who already fixed those problems.
In other words, it’s impossible to attract visitors to your site and establish a steady flow of organic traffic without proper indexation. Not to mention, you can’t generate revenue if your website isn’t visible in search.
Even if you follow all the ‘rules,’ there are no guarantees that your content will be shown in search results. Ultimately, Google decides what should and should not be indexed. But to increase the chances of proper indexation, you should always:
- ensure your website has a clear structure
- add smart interlinking, avoid the orphan pages
- don’t forget to keep your XML sitemap up-to-date
- use manual or automated solutions to speed up the indexing
- publish and maintain high-quality content
- run regular tech SEO audits
Key Reasons for Indexation Issues
Identifying the underlying cause of an indexing issue can be tricky. So let’s explore why they occur, starting with content-related problems.
Content-Related Issues
Duplicate or very similar content
Google has always taken a hard stance on duplicate content. So, if your content is a close or identical match to other material on the web, the bot may decide to disregard it. The same goes for spun or synonymized content. If your article shows the symptoms of a bad rewrite – unusual word choice, awkward phrasing – the crawler may refuse to index it.
Content that offers fresh perspectives on a popular topic has a higher chance of being indexed. But to rule out blatant duplication in your content, use plagiarism checker tools like Copyleaks, Serpstat Plagiarism Checker, or Copyscape.
Low-quality content
Indexing issues can be a sign of low-quality content. If your pages are riddled with grammar mistakes or your blog posts lack structure, Googlebot won’t see the point in indexing them.
But readability isn’t the only factor. For content to be considered high-quality, it must also provide value to the reader.
So, does your content answer the main question of a reader? Is it repetitive or boring? Is it fluffy or unfocused? Has it been written for machines instead of humans? If so, this might be why your content piece isn’t being indexed, and you could benefit from using a tool to assess content quality.

Grammarly is a great option. Apart from helping you eliminate grammar mistakes, it will make your copy clearer and more concise.
Technical Issues
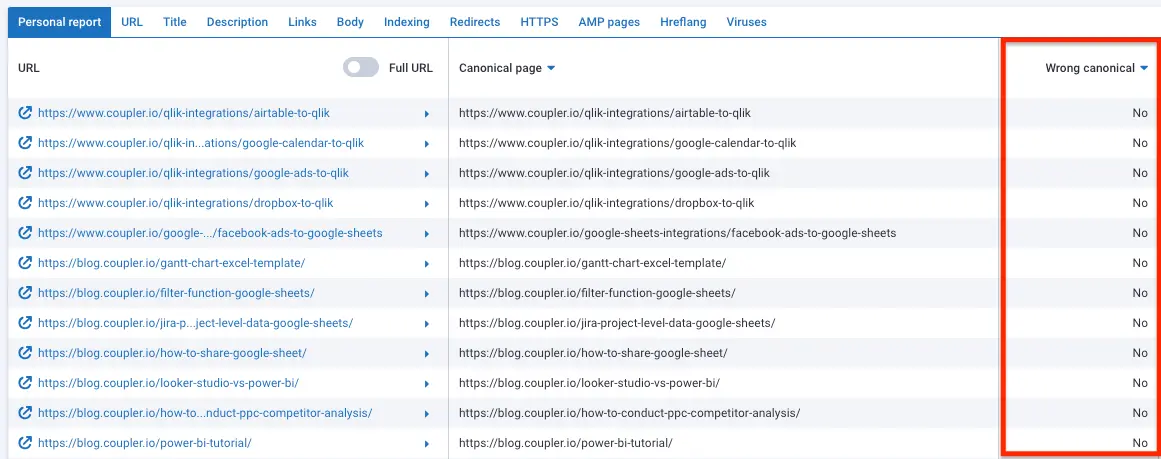
Wrong canonicals
The wrong or empty canonical on the page can lead to significant problems. This can be the reason for your indexing issue. The good news? It’s possible to validate canonicals with Serpstat’s site audit feature:
Orphaned pages
Pages with 0 internal backlinks is another common problem. Ideally, your site structure should resemble a tree, where each page has several internal backlinks. For instance, a typical pricing page would contain internal links to your ‘sign up’ and ‘contact us’ pages, among many others. This interconnectedness increases the visibility to crawlers and improves chances to be indexed.
To quickly identify orphaned pages, use Screaming Frog Spider. It will allow you to crawl the whole domain and spot out the orphans.
Soft 404s
Another reason for indexing issues is the presence of soft 404s on your site. For example, this can happen when you have custom 404 pages that don’t return the suitable response code to Googlebot. Or when the page contains minimal content, the crawler mistakenly interprets it as soft 404. The problem for such pages is not being out of index but being indexed instead because crawlers will waste effort on unnecessary pages that users don’t need to see.
Check your Google Search Console (GSC) reports for URLs returning soft 404 errors. Depending on your specific case, you may need to change server configurations, make a redirect, or add new content to the page.
Crawl budget limits
Googlebot spends a fixed amount of resources crawling each website. If a big chunk of its budget goes to a handful of pages, there won’t be enough capacity for the crawler to capture other content on your site. So, make sure to have a proper website structure with smart interlinking, moderate the content you need to be crawled and avoid unnecessary content from being crawled by the search bots.
The overuse of the crawl budget can happen due to multiple reasons and this topic is broad enough for a separate article. Try using a website crawler tool like JetOctopus or Netpeak Spider to perform a full log analysis. It may provide you with some insights.
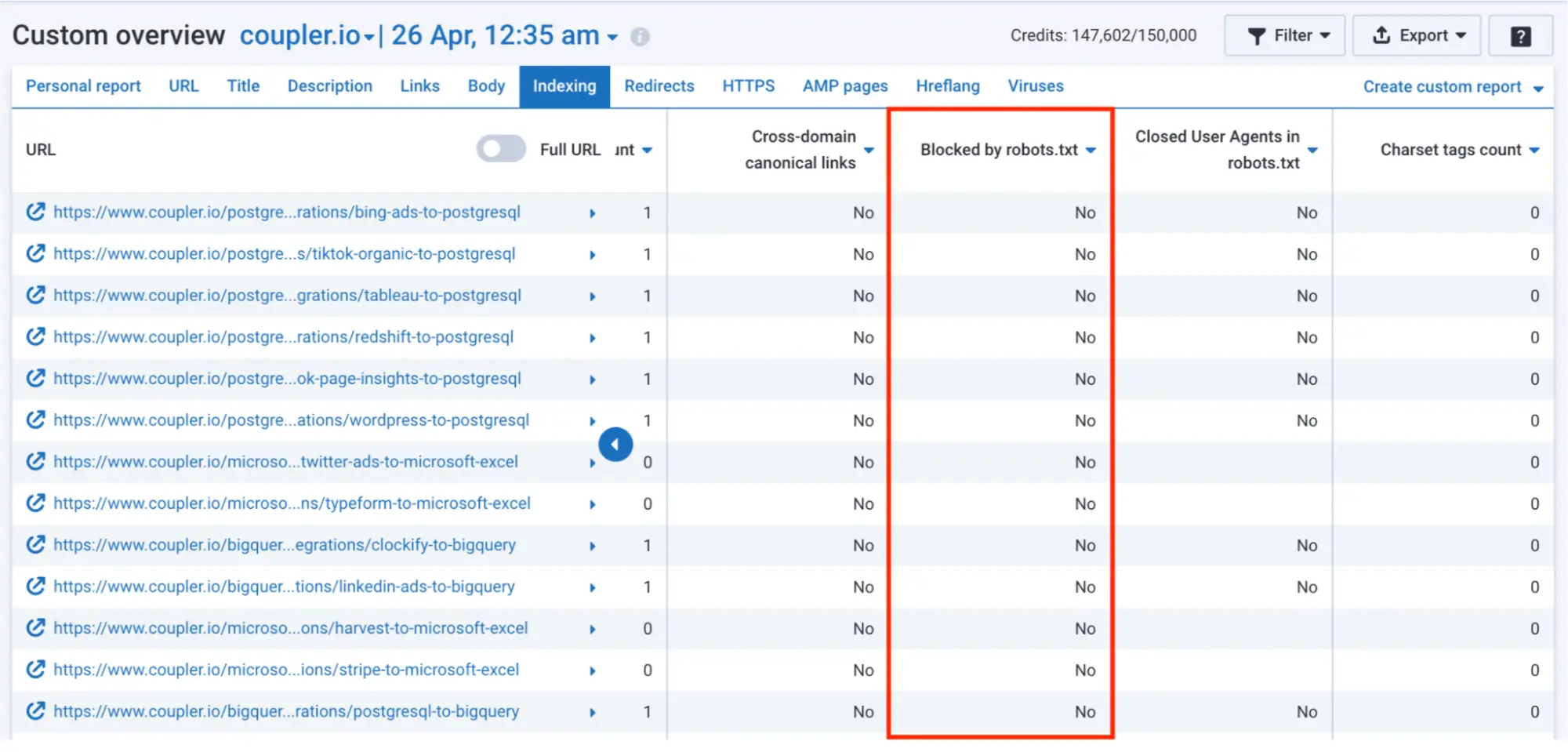
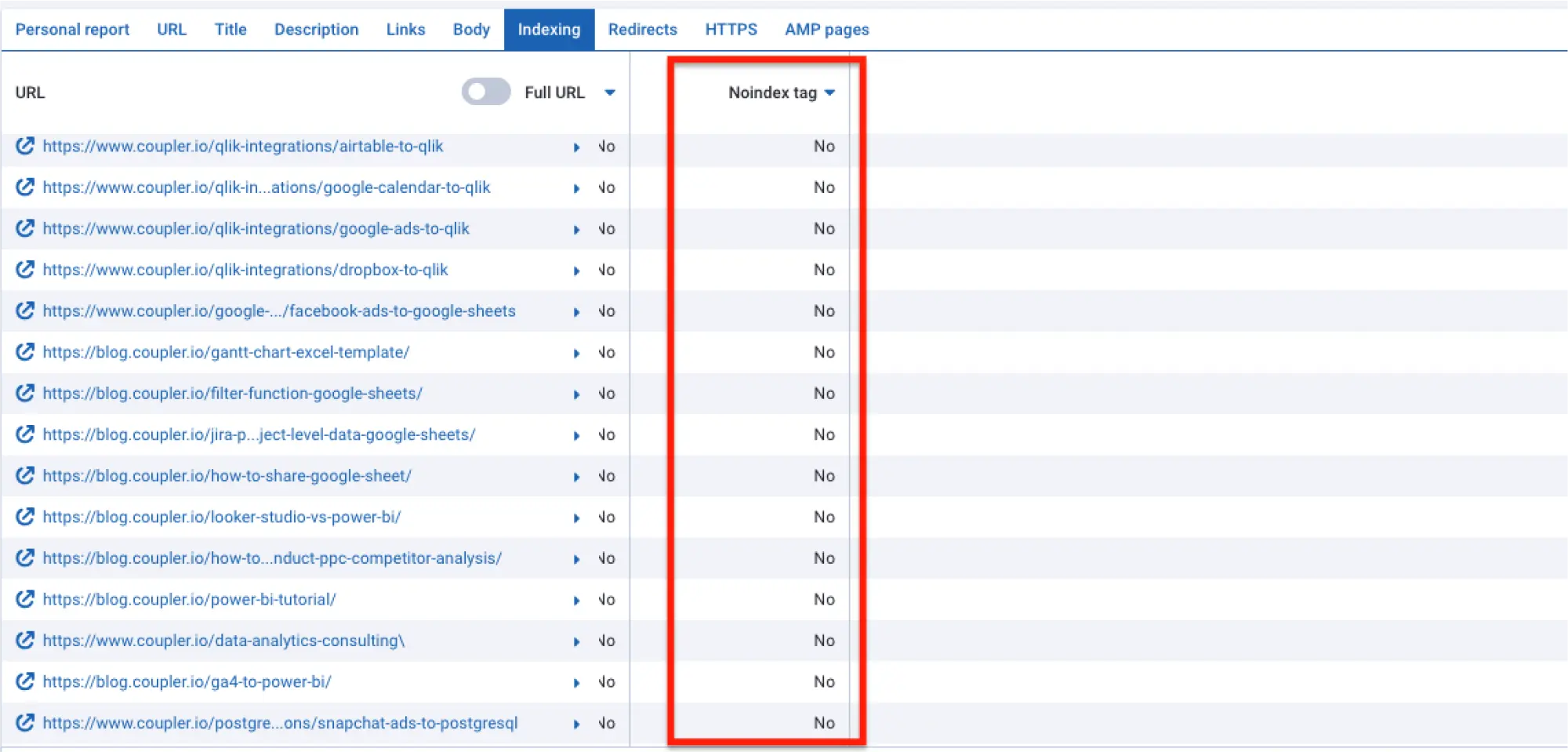
URL blocked by robots.txt or with a ‘noindex’ tag on the page
Maybe the crawler isn’t indexing your content because the page is telling Googlebot to ‘skip’ it. This could be due to robots.txt, telling Google the URL isn’t accessible, or an irrelevant ‘noindex’ tag. These are usually accidents or leftover safeguards from when your site was in development.
You can quickly check for these blockers manually by inspecting the robots.txt file or the page source code. If you have projects with a large number of pages, Serpstat can save you time.
Here’s an example from Serpstat’s indexing overview page:
Bonus
Google guidelines violation
Google has several policies to prevent spammy content from appearing in search results.
Any attempt to ‘game the system’ can prompt Google to exclude your content from its database. Examples include stuffing your pages with keywords, link spam, incorrect use of generative AI to scale your content production, etc.

There are no real shortcuts to building a sustainable SEO strategy. It’s more rewarding in the long term to work within Google’s guidelines. To rule out a potential violation, check the full list of spam policies.
Bugs in Google Search algorithm
Sometimes the issue is completely out of your control, and that’s the case with bugs. Maybe you’ve noticed a sudden drop in traffic with no clear cause. It could be a sign you’re dealing with a bug in the Google algorithm.
You might find a temporary workaround, but there is no one-size-fits-all solution. We often just have to wait for Google to fix the issue.
How to Identify the Problem with Indexing
Manual Approach via Google Search and GSC
Sometimes, unraveling an indexing issue requires manual investigation. For this task, you can use Google’s tools, Search and GSC.
Google Search
The first approach is pretty straightforward, and it’s the least time-consuming option if you need to check 10-20 pages.
Go to the search bar, and type in the search operator ‘site’ + the URL you want to check. For example, site:https://www.coupler.io/sources. If the URL is in the Google index, it will appear in the list of results – simple as that.
Google Search Console
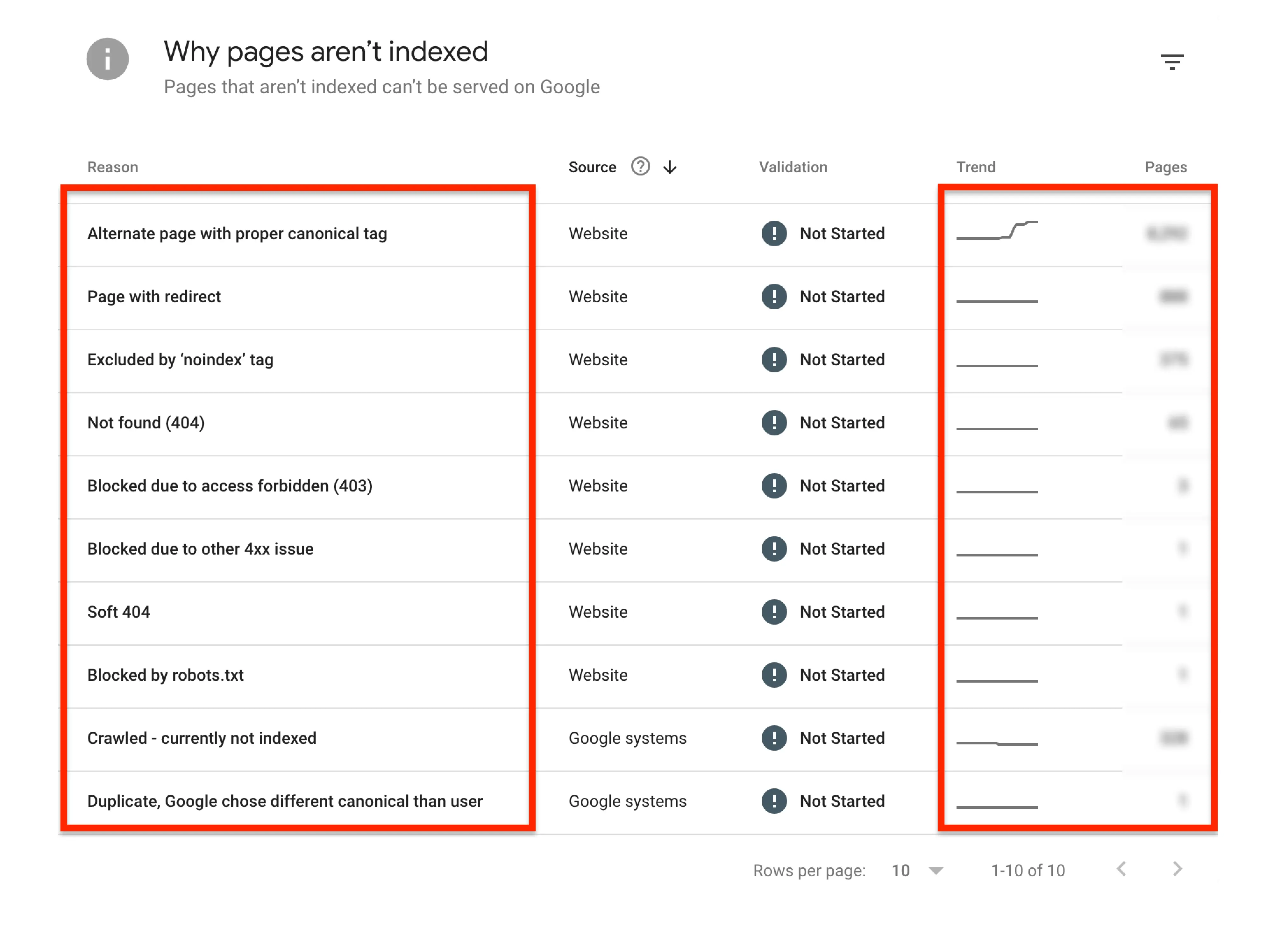
If you have an e-commerce business and your site has hundreds or thousands of pages, it’s better to check the Page Indexing Report in GSC and start your investigation there. Not only will you get a round-up of non-indexed pages, but it will also tell you exactly why those pages have been skipped.
Self-Updating Indexing Status Report Using Coupler.io
Nobody has time to monitor page indexing statuses 24/7. But in certain situations, not paying close attention to those statuses can lead to serious business losses.
Take a recent case where Google released a Core update with a bug. Many businesses saw their pages deindexed at random. This triggered a drop in organic traffic – for some, it translated to a loss of revenue. Google updates are becoming more frequent, and the stakes only get higher.
That’s why it makes sense to automate the index status reporting. You only need three tools to set this automation up:
- Google Search Console
- Coupler.io, a reporting automation solution
- Google Sheets or another destination for your indexing report
Start by setting up a free Coupler.io account. Then, navigate to the importers page in the Coupler.io main interface and click ‘add importer.’ It will open a page where you need to pick your Google Search Console as a source and the desired destination, for example, Google Sheets.
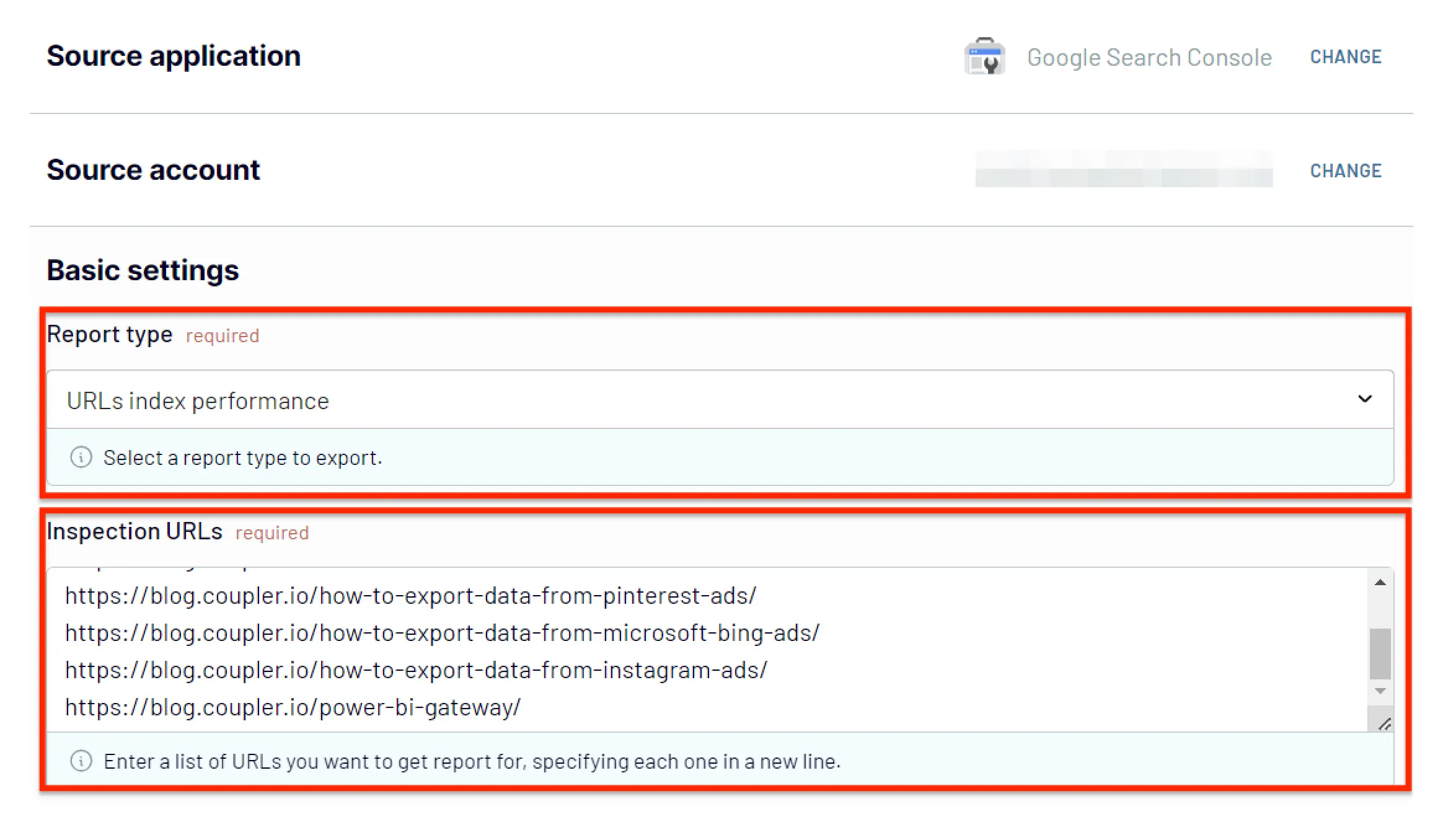
Then connect your Google Search Console account, select the sites you need to check, and choose “URLs index performance” as the report type. In the Inspection URLs field, enter a list of URLs you want to get the report for.
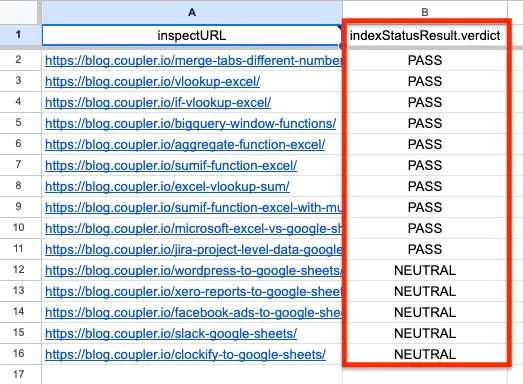
Follow the remaining steps to organize data in your report, e.g., hide unnecessary columns and load them to the chosen destination. Once the importer is running, you will get an auto-updating report that looks like this:
Don’t forget to configure the report to update on a schedule (daily, weekly – whatever works for you). And if you want to improve your SEO reporting overall, here are some more SEO report templates to get you started.
Serpstat to Identify Indexing Issues
Serpstat is an SEO management platform with a specific indexing inspection feature. This built-in tool connects to your GSC and lets you enter up to 100 URLs at a time for index verification. Then it gives you a list of inspection results like ‘index status results’, ‘amp results’, ‘mobile usability results’, and ‘rich results’.
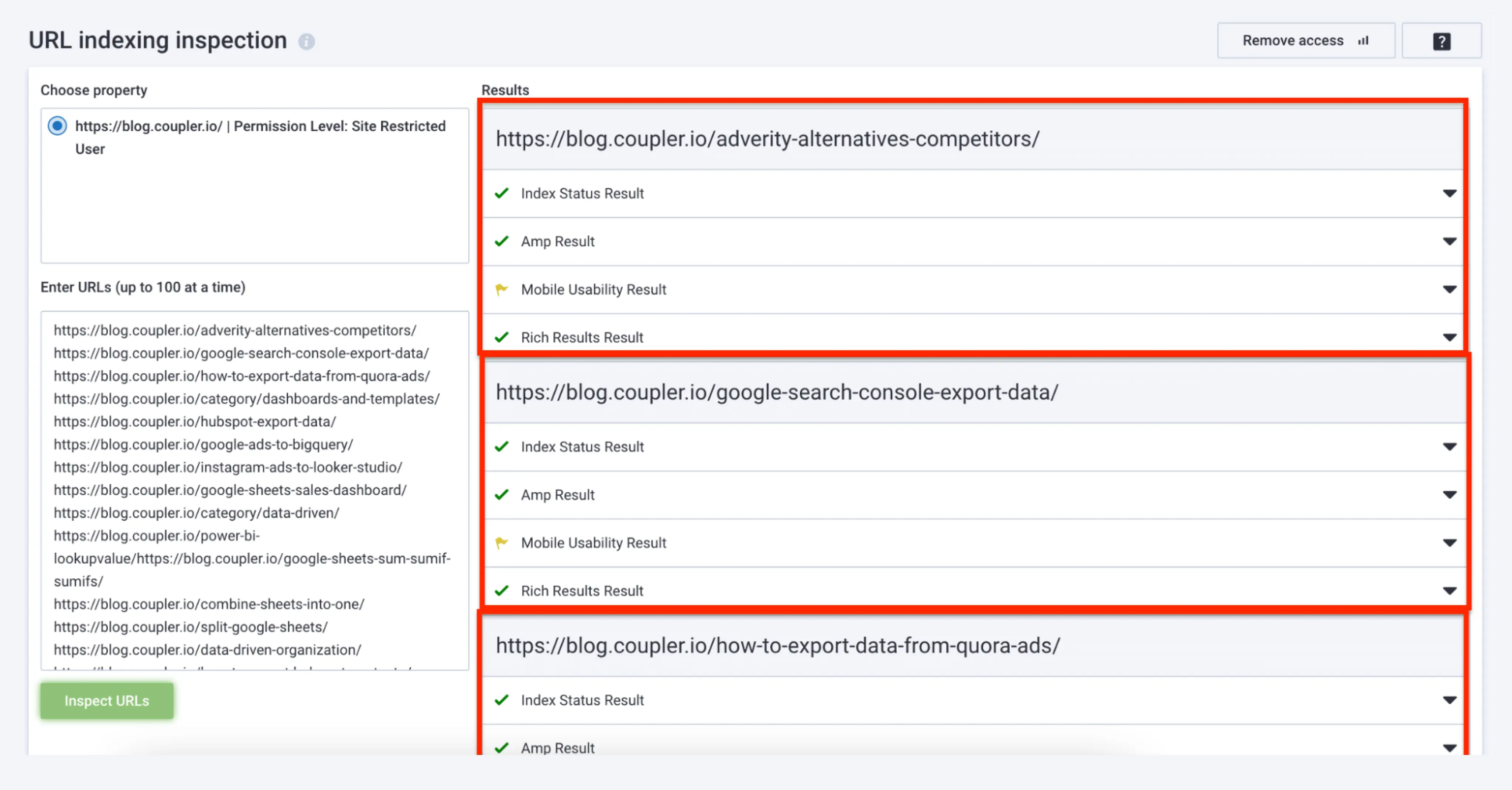
Can you Avoid Indexation Issues?
Even the most seasoned SEO experts struggle with indexing problems from time to time. As I explained, there are many reasons why these issues occur. It might be a technical mistake, a bug in the search, or something missing from the content. But there’s always a solution, as long as you know where to look.
The right set of tools and approaches can help. So, when you’re facing an indexing issue, you can:
- conduct a full-scale technical analysis
- validate the content quality
- check the changes in Google’s guidelines to rule out potential violations
- set up automated indexing status reporting after fixing the issues
Here’s hoping you solve that pesky indexing problem soon!